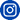
The Legend-class USCGC Stratton (WMSL 752) sails with Philippine Navy’s Gregorio del Pilar-class patrol ship BRP Ramon Alcaraz (PS-16) (former USCGC Dallas) and Philippine Coast Guard Vessel BRP Melchora Aquino (MRRV-9702) as part of a division tactics exercise in the Sulu Sea, May 20, 2025. Stratton is deployed and assigned to Destroyer Squadron (DESRON) 15, the Navy’s largest DESRON and the U.S. 7th Fleet’s principal surface force. The U.S. Coast Guard has operated in the Indo-Pacific for more than 150 years, and the service is increasing efforts through targeted bilateral patrols with our national security cutters, fast response cutters, and other activities conducted in support of maritime missions to enhance our regional partnerships. (U.S. Coast Guard photo by Petty Officer 3rd class William Kirk)
Below the line is a report of Alameda based USCGC Stratton’s visit to the Philippines at the start of a Western Pacific deployment. The report mentions exercising “with the Armed Forces of the Philippines and the PCG.”
“Following their departure, Stratton’s crew conducted a bilateral Maritime Cooperative Activity (MCA) …The MCA included exercises in maritime domain awareness, division tactics, maneuvering, and visit, board, search and seizure procedures.”
Following the link above we learn,
Participating units included the Legend-class cutter USCGC Stratton (WMSL-752) and a P-8A Poseidon maritime patrol and reconnaissance aircraft from the U.S. Navy, as well as the Philippine Navy’s Gregorio del Pilar-class patrol ship BRP Ramon Alcaraz (PS16); Acero-class patrol gunboats BRP Gener Tinangag (PG903) and BRP Domingo Deluana (PG905); an AW109 naval helicopter; the Philippine Air Force’s Super Tucano and Sokol helicopters; and the Philippine Coast Guard’s Teresa Magbanua-class patrol vessel BRP Melchora Aquino (MRRV 9702).
That is a pretty substantial exercise, US Navy, Philippine Navy, and Philippine Air Force in addition to US and Philippine Coast Guards.
While the Philippine Coast Guard has many of the trappings of a military service, they are not nearly as well armed as their Chinese, US, and Japanese counterparts. Their most powerful weapon seems to be .50 caliber machine guns. If they get into an armed confrontation with the Chinese, they cannot go it alone. Notably this was not a SAR exercise. Perhaps the idea was to practice coordination of support for the Philippine Coast Guard in their interactions with the Chinese, making sure the Philippine CG can communicate with the Philippine Navy and Air Force and with US assets in the area.
Army Recognition’s Naval News also has a report on the exercise which mentioned that Japanese built Philipine WPC BRP Malapascua (MRRV 4403) also participated in the exercise. “Philippine and US Naval Forces Conduct First Joint Maritime Exercise to Strengthen Indo-Pacific Maritime Security”
U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Stratton departs Philippines, commences months-long Indo-Pacific patrol
PUERTO PRINCESA, Philippines — The U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Stratton (WMSL 752) and its crew departed Puerto Princesa, Philippines, Monday, after in-port engagements and visits with the Philippine Coast Guard (PCG), the U.S. Ambassador to the Republic of the Philippines MaryKay Carlson, U.S. embassy staff, and PCG District Palawan senior leadership.
Stratton’s visit to Puerto Princesa marked the first international port call of their months-long deployment to the Indo-Pacific region.
Following their departure, Stratton’s crew conducted a bilateral Maritime Cooperative Activity (MCA) with the Armed Forces of the Philippines and the PCG within the Philippines’ exclusive economic zone. The MCA included exercises in maritime domain awareness, division tactics, maneuvering, and visit, board, search and seizure procedures.
These engagements demonstrate the U.S. commitment to maritime governance that supports security, freedom and prosperity in the region.
The U.S. Coast Guard serves as a unique instrument of national power, bridging defense, diplomacy and law enforcement to further national objectives and mutual interests with allies and partners like the Philippine Coast Guard.
During the visit, Stratton’s commanding officer, Capt. Brian Krautler, welcomed Amb. Carlson, PCG Commandant Adm. Ronnie Gil Gavan, and senior PCG leaders aboard Stratton, highlighting U.S. Coast Guard interoperability with allies.
“Our alliance with the Philippine Coast Guard has cultivated a close, collaborative maritime partnership—this is Stratton’s second deployment to the Philippines during my two years aboard as commanding officer,” Krautler said. “Our enduring partnership enables combined effects and cooperation across a broad spectrum of engagements and operations. Stratton’s deployment to the Indo-Pacific will further strengthen our relationships with allied coast guards and services throughout the region.”
The U.S. Coast Guard works closely with regional allies to deliver a broad range of capabilities in support of a prosperous and secure Indo-Pacific. Multilateral operations like the at-sea MCA and in-port engagements enhance cooperation, improve interoperability and strengthen readiness.
While moored, Krautler and Stratton’s leaders also met with the WESTCOM Commander PCG District Palawan for a pre-sail planning meeting to discuss bilateral search and rescue exercises (SAREX) to enhance cooperation. At-sea operations and exercises with the Philippine Coast Guard will strengthen the ability to execute coordinated maritime operations and enhance overall mission readiness.|
The U.S. Coast Guard’s commitment to a prosperous and secure Indo-Pacific requires working closely with regional allies, allowing the service to improve its logistics flexibility to better deliver a broad range of capabilities.
During the patrol, Stratton is scheduled to engage with regional partners and participate in joint operations aimed at enhancing maritime safety and security. Throughout its Indo-Pacific deployment, Stratton is assigned to Destroyer Squadron (DESRON) 15, the Navy’s largest DESRON and the U.S. 7th Fleet’s principal surface force. DESRON 15 regularly assumes tactical control of surface units operating in the area.
Stratton’s port call to the Philippines marks the cutter’s third visit following stops in 2019 and 2023. Consistent U.S. Coast Guard national security cutter deployments to the region demonstrate the U.S. commitment to strong maritime governance that supports security, freedom and prosperity in the Western Pacific.
Commissioned in 2012, Stratton is one of ten Legend-class national security cutters and one of four homeported in Alameda, California. National security cutters are 418 feet long, 54 feet wide and have a 4,600 long-ton displacement with a top speed of 28 knots, a range of 12,000 nautical miles and can hold a crew of up to 170. National security cutters routinely conduct operations throughout the Pacific, where their combination of range, speed and ability to operate in extreme weather provides mission flexibility.
The namesake of U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Stratton is Capt. Dorothy Stratton, who led the service’s all-female reserve force during World War II. Dorothy Stratton was the first female commissioned officer in the Coast Guard and commanded more than 10,000 personnel. The ship’s motto is “We can’t afford not to.”